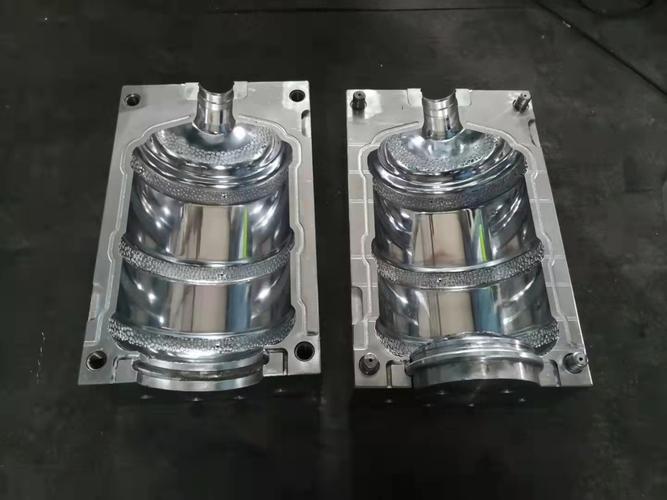
1. Why Custom Plastic Bottle Blow Molds
2. Plastic Bottle Blow Mold Processing Technologies
- CNC Milling (3-Axis & 5-Axis): Shapes mold cavities and cores from solid blocks with high precision, creating complex geometries (contoured sides, internal threads) and tight tolerances (±0.02mm). 5-axis systems handle undercuts and multi-angle features in a single setup.
- EDM (Electrical Discharge Machining): Uses electrical discharges to cut intricate details (fine logos, micro-textures) in hardened steel, ensuring sharp, precise features that resist wear during high-volume production.
- Grinding & Polishing: Finishes mold surfaces to mirror-like smoothness (Ra 0.02μm) to prevent plastic sticking and ensure bottles have glossy, blemish-free exteriors. Critical for clear containers (water, cosmetics).
- Laser Engraving: Creates detailed surface textures or logos with micron-level precision, ideal for branding elements that require consistent reproduction across thousands of bottles.
- 3D Printing (Prototyping): Builds mold prototypes from resin or metal to test bottle designs before final production, accelerating development cycles and reducing costly errors.
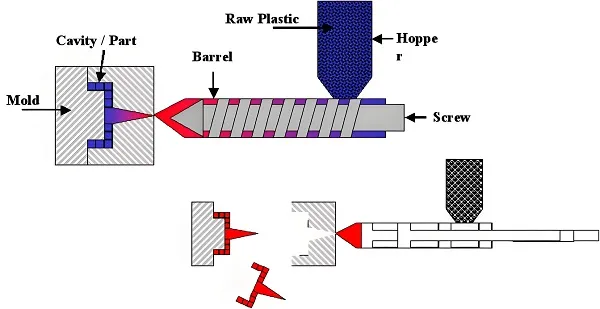
3. Plastic Bottle Blow Mold Processing Flow
- Design & Engineering: Collaborate with clients to finalize bottle specifications (volume, material, features) and mold requirements (number of cavities, cooling channel layout). Use CAD software to create 3D models and simulate the blow molding process to optimize wall thickness distribution.
- Material Selection: Choose mold materials based on production volume and plastic type—aluminum for low-to-medium runs (100,000+ bottles), P20 steel for medium volumes, and H13 tool steel for high-volume production (1 million+ units) with abrasive materials.
- Mold Base Fabrication: Machine the mold base (frame) to house cavities, cores, and cooling systems, ensuring compatibility with the client’s blow molding machine (clamp size, alignment pins).
- Cavity & Core Machining: Use CNC milling and EDM to shape the mold’s inner cavities (bottle exterior) and cores (defining neck/opening details), incorporating vents to release trapped air during molding.
- Cooling System Integration: Drill or mill channels to circulate water or oil, controlling mold temperature (typically 10–60°C) to ensure uniform cooling and reduce cycle times.
- Surface Finishing: Polish cavity surfaces to the desired texture (glossy, matte, or textured) and assemble components (guide pins, ejectors) to ensure smooth operation.
- Testing & Calibration: Run trial productions to verify bottle dimensions, wall thickness, and surface quality, adjusting cooling times or cavity dimensions as needed to meet specifications.
4. Plastic Bottle Blow Mold Materials
- Aluminum Alloys (7075, 6061): Lightweight and cost-effective for low-to-medium production runs (100,000–500,000 bottles). Excellent thermal conductivity ensures fast cooling but offers lower wear resistance than steel.
- P20 Tool Steel: Balances durability and cost for medium-volume production (500,000–1 million bottles). Better wear resistance than aluminum, making it suitable for HDPE or PP bottles.
- H13 Tool Steel: High-strength and heat-resistant, ideal for high-volume production (1 million+ bottles) or abrasive materials (PET with additives). Resists corrosion and maintains precision over extended use.
- Beryllium Copper Alloys: Superior thermal conductivity (2–3x that of steel) reduces cycle times by 20–30%, used for complex molds requiring rapid, uniform cooling (contoured bottles, multi-cavity designs).
5. Plastic Bottle Blow Mold Applications
- Food & Beverage Packaging: Molds for water bottles, juice containers, and sauce bottles, often using PET or HDPE with smooth surfaces to maintain product purity and enable labeling.
- Personal Care & Cosmetics: Custom molds for shampoo bottles, lotion containers, and perfume vials, featuring intricate details (embossed logos, frosted finishes) to enhance brand appeal.
- Household & Cleaning Products: Molds for detergent bottles, spray bottles, and bleach containers, engineered with chemical-resistant materials (HDPE) and secure thread (threads) to prevent leaks.
- Pharmaceutical & Medical Packaging: Molds for pill bottles, liquid medication containers, and hand sanitizer bottles, meeting strict standards (FDA, ISO 15378) for cleanliness and precision.
- Industrial Packaging: Large-scale molds for chemical drums, lubricant bottles, and agricultural containers (10–20L), using durable H13 steel to handle heavy-wall HDPE or PP.
6. Plastic Bottle Blow Mold Performance Additions
- Ventilation Systems: Microscopic vents (0.02–0.05mm) prevent air traps during molding, eliminating defects like dimples or incomplete filling, critical for clear or high-gloss bottles.
- Texturing & Branding: Laser-etched logos, patterns, or grip textures that transfer seamlessly to the bottle surface, enhancing brand recognition without compromising mold durability.
- Multi-Cavity Designs: Molds with 2–32 cavities (depending on bottle size) to increase production output, with balanced cooling channels ensuring uniform wall thickness across all cavities.
- Quick-Change Features: Modular components (neck inserts, cavity plates) that allow fast switching between bottle designs, reducing downtime for brands with multiple product lines.
- Corrosion Resistance: Chromium or nickel plating protects mold surfaces from aggressive materials (acids, solvents), extending lifespan and maintaining surface finish in chemical packaging applications.
7. Plastic Bottle Blow Mold Common Questions
How long does a custom blow mold last?
Lifespan depends on material and usage: aluminum molds last 100,000–500,000 cycles; P20 steel molds 500,000–1 million cycles; H13 steel molds 1–5 million+ cycles. Proper maintenance (cleaning, lubrication) can extend life by 20–30%.
What’s the difference between single-cavity and multi-cavity molds?
Single-cavity molds produce one bottle per cycle, ideal for low-volume or large-format bottles (5L+). Multi-cavity molds (2–32 cavities) increase output for small-to-medium bottles (500ml–2L), reducing per-unit production costs for high-volume runs.
Can custom molds handle different plastic materials?
Yes, but material properties affect mold design: PET requires higher cooling rates (faster cycle times) than HDPE, while PP may need adjusted cavity pressures. Molds can be optimized for specific resins to ensure proper shrinkage control.
How long does it take to produce a custom blow mold?
Simple single-cavity molds take 3–4 weeks; complex multi-cavity molds with intricate details take 6–8 weeks. Rush orders can be completed in 2–3 weeks with expedited machining.
How do molds affect bottle quality?
Mold surface finish directly impacts bottle appearance—polished molds create glossy bottles, while textured molds produce matte surfaces. Proper cooling channel design ensures uniform wall thickness, preventing weak spots or deformation.