Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Overview of Pin Injection Molding
- Equipment and Components for Pin Injection Molding
- Process Flow of Pin Injection Molding
- Key Process Parameters and Optimization
- Common Issues and Solutions
- Maintenance and Servicing
- Safety Operating Procedures
- Appendix

1. Introduction
Pin injection molding is a vital method within the injection molding industry, utilizing precision pin assemblies within molds to achieve the injection, pressure holding, and ejection of molten plastic. This manual aims to provide comprehensive guidance on pin injection molding techniques, assisting technicians in better understanding and applying this technology.
2. Overview of Pin Injection Molding
Pin injection molding is an efficient plastic molding process suitable for producing plastic products of various shapes and sizes. During the molding process, pins serve as crucial components in the mold, controlling the flow of molten plastic, maintaining pressure within the mold, and facilitating the ejection of the molded product.
3. Equipment and Components for Pin Injection Molding
Primary Equipment:
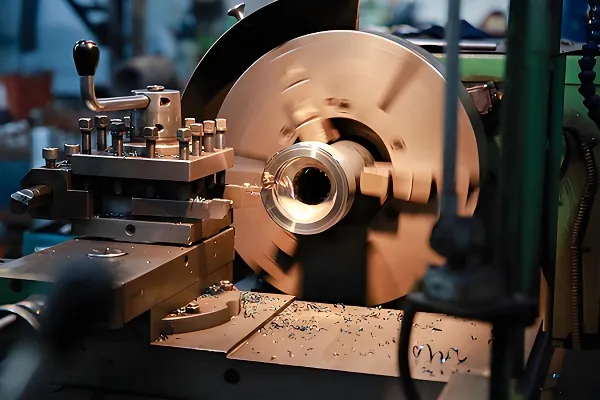
- Injection molding machine: Provides the high-temperature, high-pressure environment required for molten plastic.
- Mold: Contains the pin assembly for shaping the plastic product.
- Temperature control system: Regulates the temperature of the mold and injection molding machine.
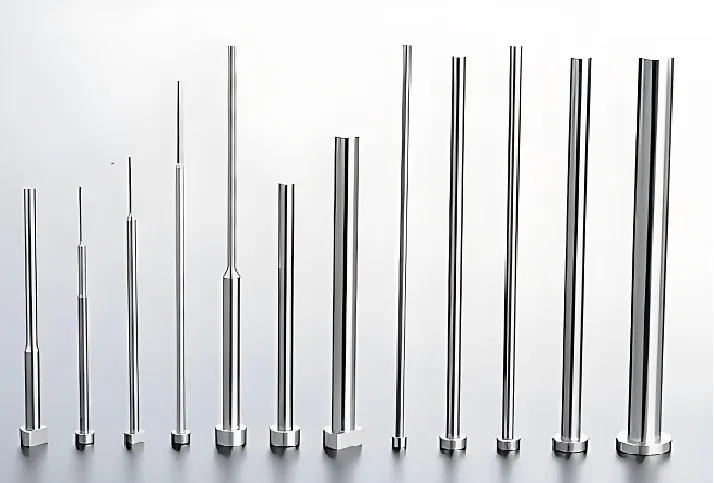
Key Components:
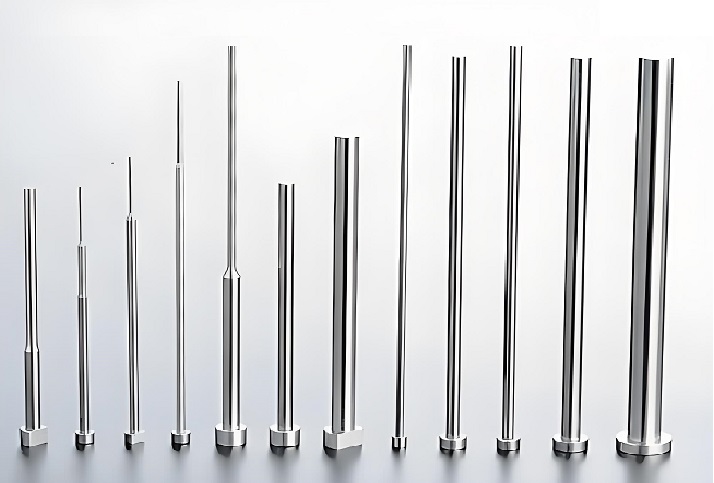
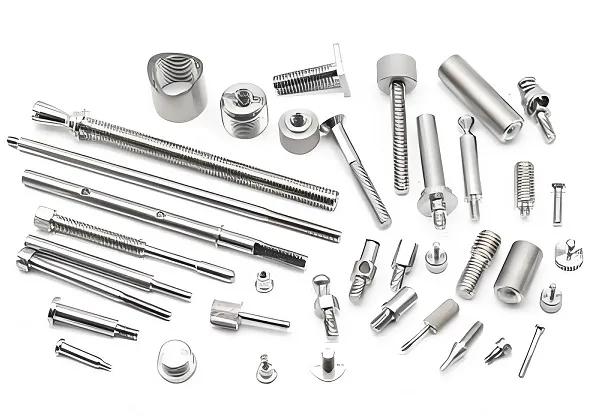
- Pins: Typically made of high-speed steel, used to eject the molded product from the mold.
- Pin plate: Holds the pins and transfers force.
- Hydraulic or pneumatic system: Controls the movement of the pins.
4. Process Flow of Pin Injection Molding
- Mold Closing: Tightly closes the mold in preparation for the injection process.
- Injection: Molten plastic is injected into the mold cavity through the injection molding machine nozzle.
- Pressure Holding: Maintains a certain pressure within the mold during the cooling and solidification of the molten plastic to ensure product density.
- Material Reserve: Replenishes molten plastic for the next injection.
- Screw Retreat: Reduces pressure at the screw tip to prevent overflow.
- Cooling: Exchanges heat through cooling water in the mold to solidify the molten plastic.
- Mold Opening: Opens the mold to prepare for ejection.
- Ejection: The pin assembly pushes the molded product out of the mold.
5. Key Process Parameters and Optimization
Process Parameters:
- Injection Temperature: Adjusted according to the plastic type to ensure a molten state.
- Injection Pressure: Controls the flow rate of molten plastic.
- Pressure Holding Time: Ensures product density and avoids shrinkage.
- Cooling Time: Allows sufficient solidification of the molten plastic.
Optimization Suggestions:
- Adjust pin positions and quantities based on product shape and size.
- Optimize mold design to improve production efficiency.
- Strictly control process parameters to ensure product quality.
6. Common Issues and Solutions
Issues:
- Surface defects on the product (e.g., bubbles, cracks).
- Noticeable pin marks.
- Mold damage.
Solutions:
- Adjust injection temperature and pressure to ensure uniform flow of molten plastic.
- Optimize pin design to reduce marks.
- Regularly inspect and maintain the mold to prevent damage.
7. Maintenance and Servicing
- Regularly check the wear and tear of the pin assembly and mold.
- Clean the mold and pins to keep their surfaces smooth.
- Lubricate the pin assembly to ensure smooth movement.
- Perform regular maintenance on the injection molding machine to ensure stable operation.
8. Safety Operating Procedures
- Check equipment for completeness and safety before operation.
- Follow operating procedures to avoid misoperation.
- Wear protective equipment to prevent burns and mechanical injuries.
- Do not touch moving parts while the equipment is running.
9. Appendix
Common Plastic Material Parameters:
- ABS: Injection temperature 200-250°C, recommended 210-225°C.
- PC: Injection temperature 280-320°C, recommended 300-310°C.
- POM: Injection temperature 180-230°C, recommended 205°C.
Pin Materials and Properties:
- SKD61: High hardness, wear-resistant, suitable for high-precision molds.
- SKH51: High-speed steel, heat-resistant, good toughness, suitable for high-demand pins.
Conclusion:
This manual provides comprehensive guidance on pin injection molding techniques, including equipment, process flow, key parameters, common issues, and solutions. It aims to help technicians better understand and apply this technology, improving production efficiency and ensuring product quality.