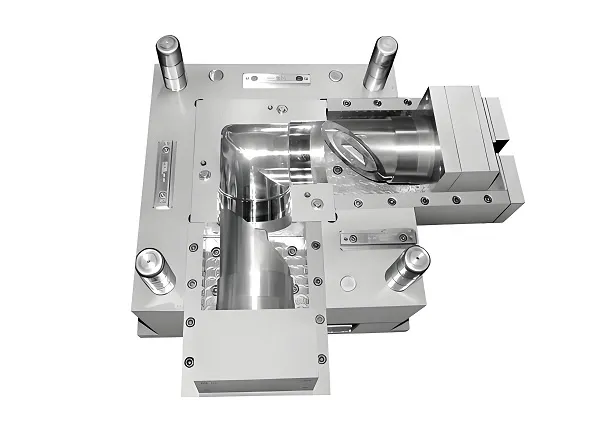
When designing parts for CNC machining, the following steps and considerations can help ensure a successful outcome:

Material selection: Choose a material that is suitable for the application and CNC machining process. Consider factors such as strength, hardness, machinability, and cost. Common materials include aluminum, steel, brass, and plastics.
Part geometry and complexity: Keep the part geometry as simple as possible to reduce machining time and costs. Avoid overly complex shapes and undercuts that may require special tooling or multiple setups.
Tolerance and surface finish: Determine the required tolerances and surface finish based on the part’s function. Tighter tolerances and smoother surfaces typically increase machining time and cost.
Fixture and clamping points: Design features or areas on the part for secure fixturing and clamping during machining. This helps prevent part movement and ensures accuracy.
Tool access: Ensure that the cutting tools can reach all areas of the part without interference. Provide sufficient clearance for tool movement and avoid deep cavities or narrow channels that may be difficult to machine.
Draft angles: Incorporate draft angles on vertical surfaces to facilitate part removal from molds or fixtures and to improve machinability.
Corner radii and chamfers: Use appropriate corner radii and chamfers to reduce stress concentrations, improve tool life, and enhance the part’s appearance.
Symmetry and balance: If possible, design the part to be symmetrical or balanced to simplify the machining process and improve part stability.
Consider multiple operations: Plan for multiple machining operations, such as roughing, semi-finishing, and finishing, to achieve the desired final shape and accuracy.
Communication with the machinist: Work closely with the CNC machinist or machining facility during the design phase. They can provide valuable input based on their equipment and expertise to optimize the design for manufacturability.
By following these guidelines and taking into account the capabilities and limitations of CNC machining, you can design parts that are efficient to produce, meet the required specifications, and result in high-quality end products.