Types of Injection Molding Bubbles
|
Bubble Type
|
Appearance
|
Common Causes
|
Detection Method
|
|
Surface Bubbles
|
Small blisters on surface
|
Moisture, air entrapment
|
Visual inspection
|
|
Internal Voids
|
Hidden internal cavities
|
Poor venting, material issues
|
X-ray, sectioning
|
|
Vacuum Voids
|
Sink marks after cooling
|
Uneven cooling, shrinkage
|
Delayed appearance
|
|
Silver Streaks
|
Silver threads on surface
|
Volatile gases, decomposition
|
Visual inspection
|
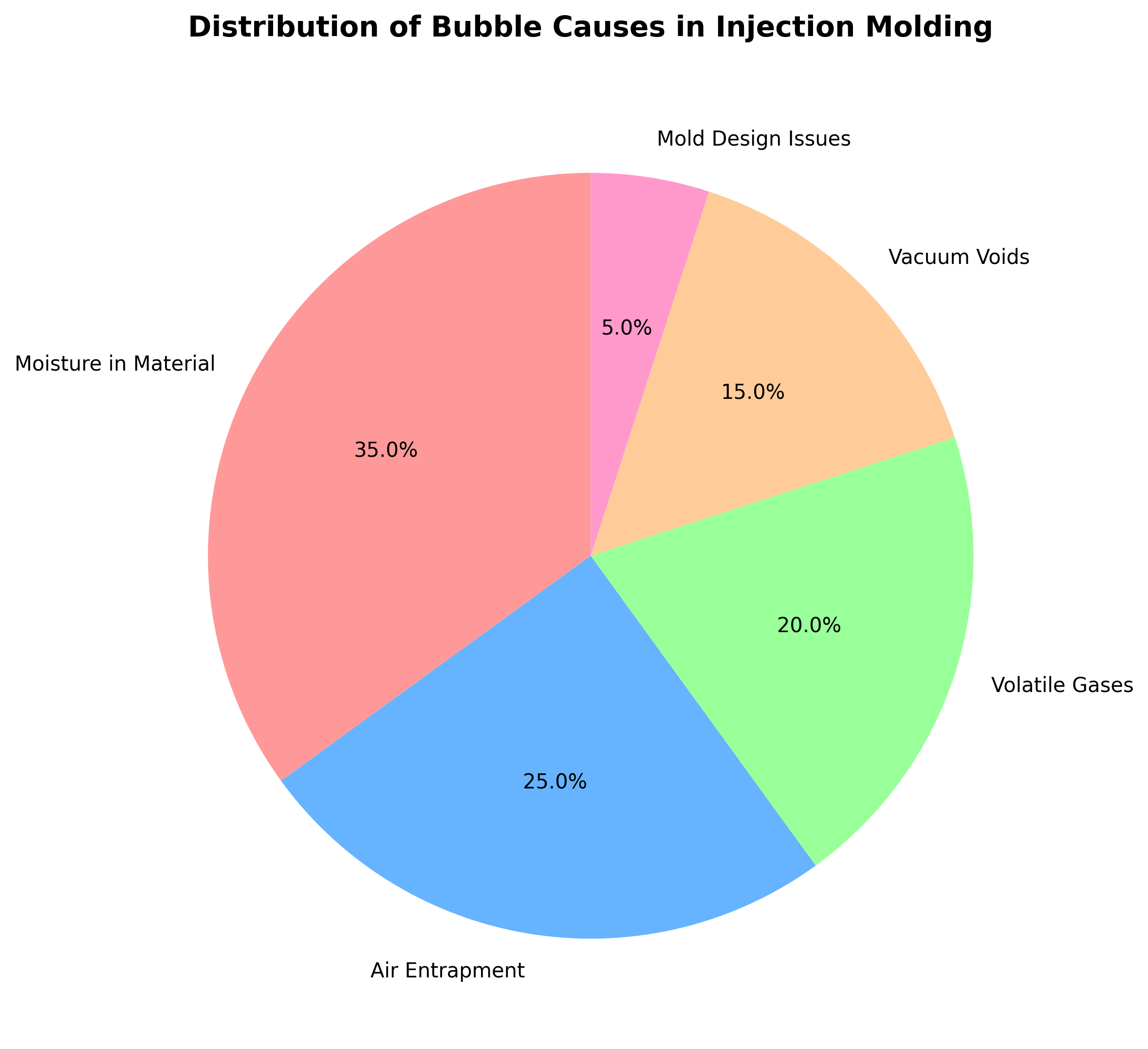
Distribution of Bubble Causes
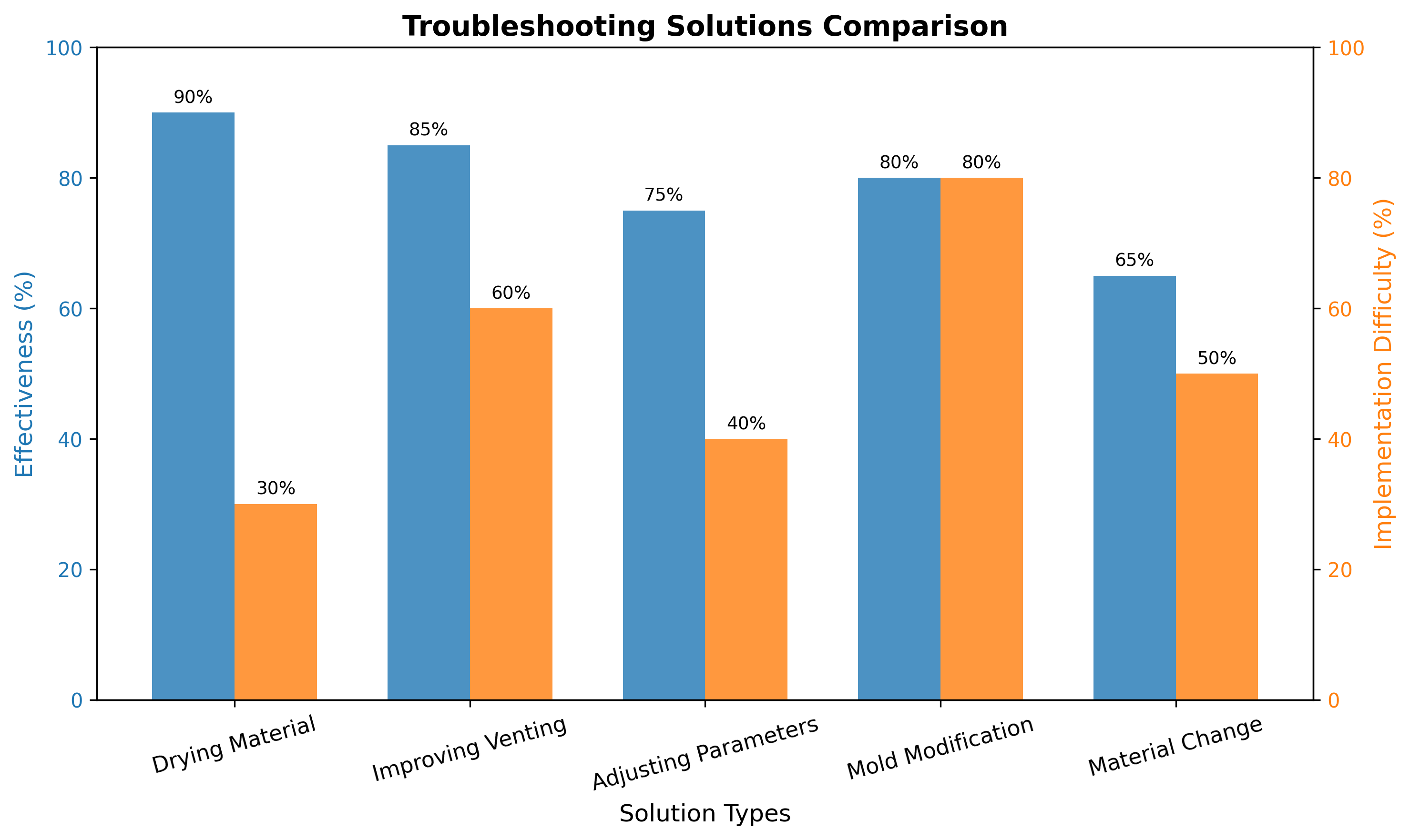
Troubleshooting Solutions Comparison
Professional Knowledge about Injection Molding Bubbles
Material-Related Causes
- Moisture Content: Hygroscopic materials (PA, PC, PET) absorb moisture, which vaporizes during heating
- Volatile Substances: Residual monomers, additives, or contaminants release gases at high temperatures
- Material Degradation: Overheating causes polymer chain breakage and gas formation
Process Parameter Issues
- Temperature Control: Excessive melt temperature leads to material decomposition
- Injection Speed: Too fast causes turbulence and air entrapment
- Pressure Settings: Insufficient injection/holding pressure fails to compact material
- Screw Parameters: High speed/low back pressure allows air incorporation
Mold Design Factors
- Venting System: Inadequate venting channels (0.02-0.05mm depth recommended)
- Gate Design: Improper location or size causes flow imbalance
- Runner System: Restrictive flow paths trap air
- Cooling Uniformity: Uneven cooling creates temperature gradients
Environmental Factors
- Humidity Control: High ambient humidity affects material moisture content
- Contamination: Oil, dirt, or release agents introduce foreign substances
- Storage Conditions: Improper material storage leads to moisture absorption
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: How can I distinguish between different types of bubbles?
Q2: What is the most effective solution for moisture-related bubbles?
Q3: How should I design mold venting for bubble prevention?
Q4: What process parameters should I adjust first for bubbles?
Q5: Can recycled materials cause more bubbles?
Q6: How does mold temperature affect bubble formation?
Q7: What is the minimum drying requirement for hygroscopic materials?
Q8: How can I prevent air entrapment during injection?
All experimental data presented in this paper are derived from controlled production environments and standardized test procedures. However, due to differences in equipment models, material batches, and on-site operating conditions, readers are advised to verify and adjust technical parameters according to their specific application scenarios before practical implementation.
The research results and technical insights shared herein are based on the author’s professional experience and experimental observations. The author and the affiliated institution shall not be liable for any direct, indirect, or consequential damages (including but not limited to equipment damage, product quality issues, or production losses) arising from the improper use of the information provided in this paper.